 Click
to show/hide the parameters.
Click
to show/hide the parameters.Command |
Path |
Shortcut |
Plug-in Manager |
Tools > Plug-ins |
● Ctrl+Shift+Z (Windows) ● Cmd+Shift+Z (Mac) |
The Plug-in Manager displays three types of plug-ins:
● Custom, unobfuscated plug-ins that you create
● Third-party plug-ins, purchased from developers (obfuscated), and obfuscated plug-ins you create
● Built-in, obfuscated plug-ins that are included with the Vectorworks program
Third-party plug-ins and built-in plug-ins, which are obfuscated, may allow limited editing of the plug-in parameters and definition. Options that are not available for editing are grayed.
Custom, unobfuscated plug-ins are created and edited from the Custom Plug-ins tab of the Plug-in Manager, where you can specify the plug-in type, category, parameters, options, and code for a new custom plug-in. Plug-ins are saved as described in Plug-in file location.
To create a plug-in:
1. Select the command.
The Plug-in Manager dialog box opens.
 Click
to show/hide the parameters.
Click
to show/hide the parameters.
2. From the Custom Plug-ins tab, click New.
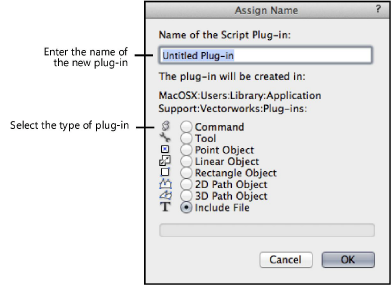
The Assign Name dialog box opens. Enter the name of the new plug-in item and select the type of the plug-in to create. Plug-in names are limited to 27 characters in length. The appropriate plug-in extension will be appended to the plug-in name. Plug-ins can contain a Python script for execution.
 Click
to show/hide the parameters.
Click
to show/hide the parameters.
3. Define the plug-in properties as described in Specifying the plug-in definition.
4. Add the new plug-in to one or more workspaces with the Workspace Editor. See Customizando Workspaces. Once the item has been added to a workspace, it is available to any open file in Vectorworks without the need for importing the associated script into the active file.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~